Persistent deciduous teeth, often known as retained baby teeth, is a dental condition in canines that can lead to various health issues if left untreated. While puppies are meant to lose their baby teeth by the time they reach approximately three months of age, some may experience the troubling phenomenon of adult teeth erupting before these primary teeth fall out. This article seeks to delve deep into the concept of persistent deciduous teeth, exploring its symptoms, causes, affected breeds, and appropriate treatments to ensure the well-being of our canine companions.
Under normal circumstances, a dog will have a total of 28 baby teeth that eventually give way to 42 adult teeth. This transition typically occurs between 14 to 30 weeks of age. It is crucial for dog owners to understand this natural progression so they can recognize when deviations happen. Observations of retained baby teeth need to be made to prevent any further complications that may arise from this condition.
Dogs suffering from persistent deciduous teeth may exhibit several oral-related symptoms that should alert their owners. Some of the most prominent signs include:
– Overbite: Misalignment in teeth can lead to significant jaw pain and eating difficulties.
– Periodontal disease: Accumulation of plaque and bacteria can occur in the presence of retained teeth, leading to infections and gum disease.
– Gingivitis: Inflammation of the gums is a common symptom, often accompanied by discomfort.
– Difficulty eating: Dogs may struggle with chewing due to overcrowding or pain in the mouth.
– Cavities and tooth decay: Unattended baby teeth can lead to severe dental caries, sometimes resulting in pus-filled cavities.
– Food retention: Particles may become lodged in gaps created by improperly aligned teeth, contributing to decay.
These symptoms can significantly impact a dog’s health and quality of life, underscoring the importance of timely veterinary intervention.
The primary culprit of persistent deciduous teeth is the failure of baby teeth to naturally exfoliate before the eruption of adult teeth. This condition is particularly common in smaller dog breeds, such as Poodles, Yorkshire Terriers, and Pugs. An elevated risk may exist due to genetic predispositions, especially in flat-faced breeds, where space constraints in the mouth can hinder normal dental development.
Besides genetics, oral health and management practices may also play an essential role. Lack of routine dental care can exacerbate problems and increase the likelihood of developing persistent teeth.
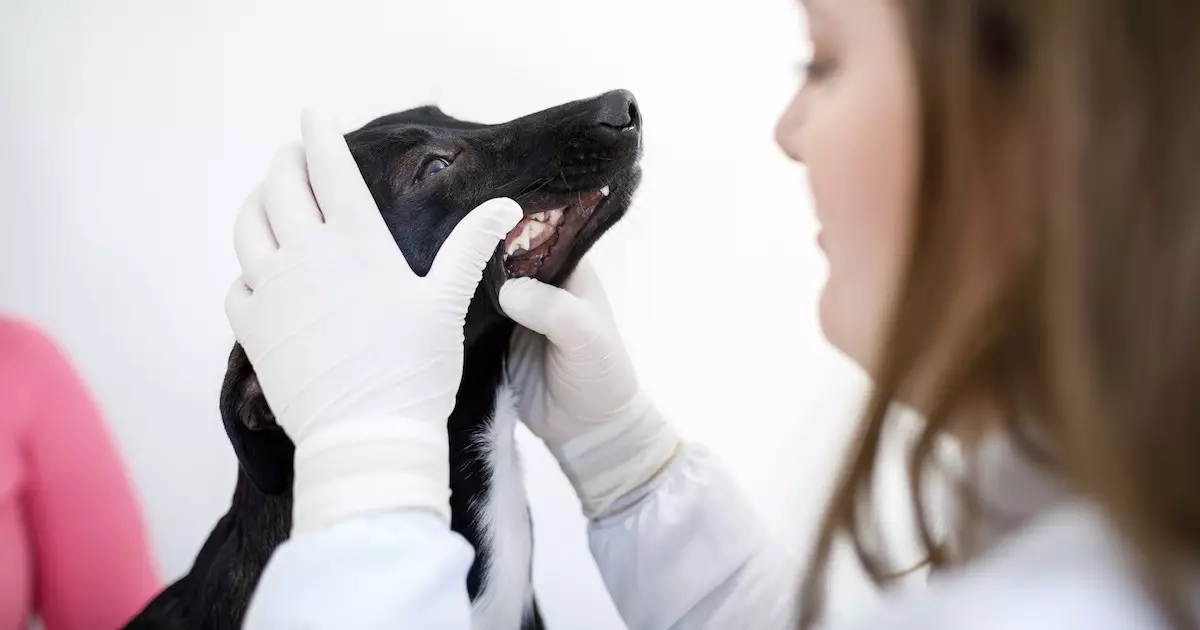
If you suspect your dog could be affected by persistent deciduous teeth, seeking a veterinarian’s approval is vital. A thorough examination of the mouth is the first step, where the vet will assess alignment, inflammation, and any presence of decay. Dental X-rays may be employed to visualize the full extent of the teeth and any underlying issues. Confirming the condition is essential as it assists in determining the best course of action for treatment.
The primary treatment for persistent deciduous teeth often involves surgical intervention to extract stubborn baby teeth. This process typically requires general anesthesia to ensure the safety and comfort of the dog. If significant jaw misalignment or overbite issues are present, further teeth removal might be necessary to restore proper function.
Post-operative recovery can vary, generally taking up to eight weeks. During this period, some dogs might experience complications in eating, necessitating the use of feeding tubes or specially formulated soft foods. Early intervention and consistent monitoring are crucial in helping your dog navigate this recovery time without lasting issues.
Preventive dental care can make a significant difference in your dog’s oral health and can help avert conditions like persistent deciduous teeth. Regularly inspecting your dog’s mouth and maintaining a consistent dental hygiene routine will go a long way in ensuring their teeth remain healthy throughout their lifetime. Conversations about dental health should be a fixture of routine veterinary visits, ensuring that problems are caught before they escalate.
Persistent deciduous teeth may pose a serious health risk to our furry friends. By being aware of the symptoms and providing timely veterinary intervention, we can help ensure that dogs live healthy and comfortable lives with optimal dental health.