Gingival hyperplasia is a dental condition in dogs characterized by the abnormal growth of gum tissue. This enlargement often results from inflammation, a common issue that can lead to more severe dental problems such as periodontal disease. While any dog can develop this condition, certain breeds are more susceptible, including Boxers, Great Danes, and Dalmatians. Understanding this condition is crucial for pet owners who wish to maintain their dog’s oral health.
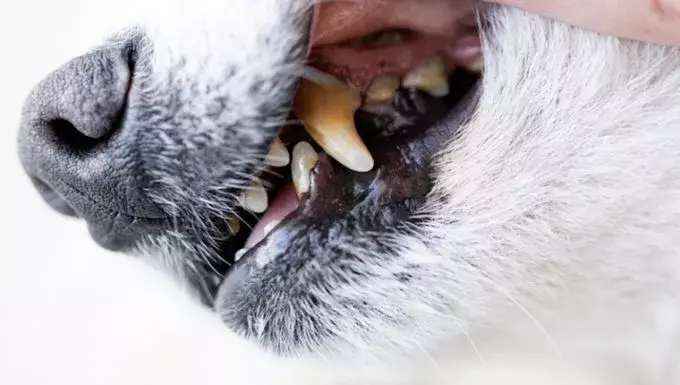
Recognizing the symptoms of gingival hyperplasia early can make a significant difference in managing the condition. Typically, affected dogs exhibit inflamed and swollen gums. These symptoms might also include:
– Thickening of the gum tissue
– Visible growths along the gum line
– Redness and bleeding of the gums
– Formation of pockets in between the teeth and gums
These issues can lead a dog to chew on their own gums, aggravating the situation and complicating recovery.
Several factors can contribute to the development of gingival hyperplasia. A primary cause is the accumulation of plaque and bacteria around the gum line, which can lead to inflammation and tissue growth. Moreover, certain breeds are genetically predisposed to this condition. Notably, breeds such as Doberman Pinschers, Collies, and Boxers are more frequently affected. Additionally, the use of immunosuppressant medications can also trigger gingival hyperplasia, as they impair the immune system’s ability to manage inflammation effectively.
If you suspect that your dog may be suffering from gingival hyperplasia, it is essential to seek veterinary care promptly. A veterinarian will conduct a thorough examination of your pet’s mouth and teeth. Diagnostic tests, such as dental X-rays and tissue biopsies, may be necessary to rule out other oral health issues or underlying conditions.
Once diagnosed, effective treatment for gingival hyperplasia typically involves a combination of surgical and non-surgical interventions. Surgical procedures aim to excise excess gum tissue, thereby alleviating pain and reducing the risk of future complications. The veterinarian may also focus on deep cleaning the dog’s teeth to remove plaque buildup and promote healthier gums.
Post-operative care is equally important, and pain management medications are typically prescribed. Following your veterinarian’s guidelines for medication administration and recovery is vital for ensuring your dog heals properly.
Preventing gingival hyperplasia largely depends on maintaining your dog’s oral hygiene. Regular dental check-ups, professional cleanings, and good home dental care can significantly reduce the risk of developing this condition. Regular tooth brushing and providing dental-friendly treats can go a long way in keeping your dog’s gums and teeth healthy.
Being vigilant about your dog’s dental health and recognizing the signs of gingival hyperplasia can lead to early intervention and effective treatment. With appropriate care, you can help your furry friend live a healthier, happier life. Have you experienced gingival hyperplasia with your dog? Sharing your experiences can be incredibly valuable for other pet owners facing similar challenges.