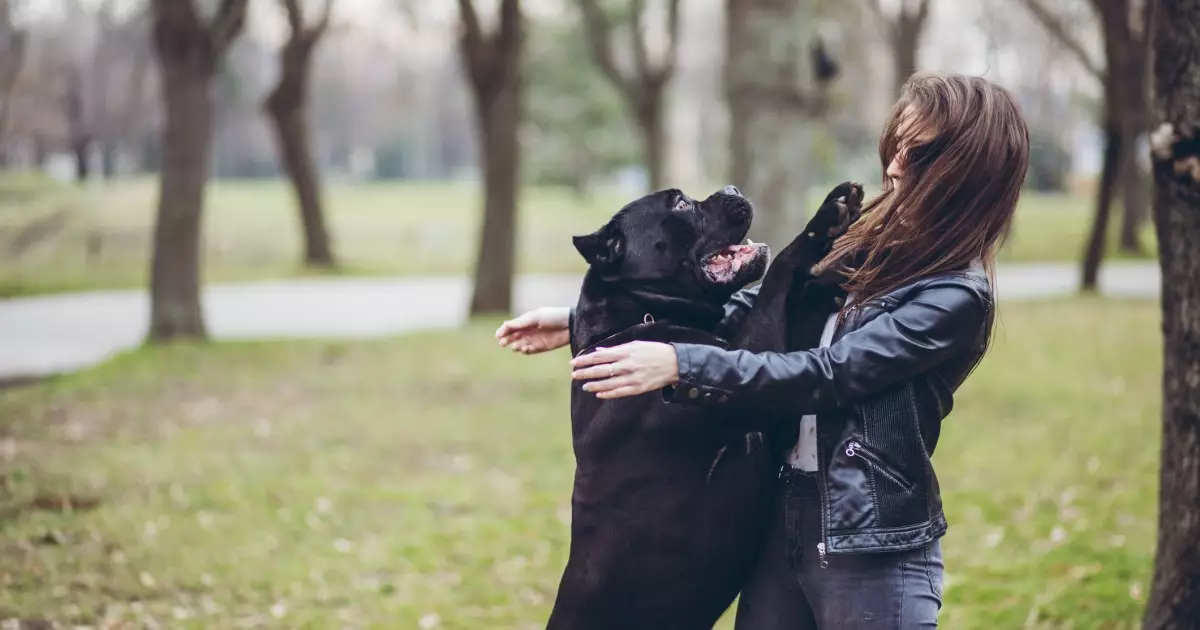
Dogs have a unique way of expressing their excitement and affection, and one of the most common manifestations of this behavior is jumping up on their owners. While this instinctive action can be charming, particularly when exhibited by small pups, it poses significant challenges as the dog grows. In this article, we will delve into the reasons behind this behavior and offer practical solutions to effectively manage and modify it.
Jumping is a natural impulse for dogs, serving two primary functions: expressing enthusiasm and facilitating social interactions. When a dog leaps into the air to greet someone, it demonstrates both excitement and a desire for closeness. Canines are instinctively drawn to the scent glands located on faces, making a jump an effective way for them to get closer for a sniff. This behavior is especially encouraged during the puppy stage, as owners often respond positively to their furry friends’ exuberance, leading to a reinforcement cycle that embeds the habit.
In many households, jumping becomes a socially accepted way for dogs to greet their humans. Owners may encourage this behavior without realizing its long-term implications, often through playful interactions on the floor. However, as dogs mature into larger, more powerful animals, the charming antics of a small pup transform into potentially dangerous behavior.
Though initially adorable, a 70-pound dog jumping on guests can pose significant risks. Not only can it lead to accidental injuries, especially for children or elderly visitors, but it can also create a chaotic atmosphere where boundaries are blurred. Therefore, understanding that what is playful in a puppy is not suitable in an adult dog becomes critical for responsible ownership.
To mitigate jumping, it’s essential to teach dogs that such behavior does not yield the desired attention or affection. This requires consistent training focused on redirecting their energy towards more acceptable behaviors. Owners must adopt a firm yet compassionate approach to discourage jumping while reinforcing alternative, desirable actions.
An effective strategy for managing exuberant jumping involves a combination of consistency and positive reinforcement. The key is to ensure that when dogs jump, they are met with a neutral or negative response—such as turning away, crossing arms, and ignoring them—rather than the affection they seek. This teaches dogs that jumping results in withdrawal of attention and becomes less appealing over time.
Once the dog is calm, the owner can initiate the desired behavior by requesting a simple “sit” command. Upon compliance, praise and gentle affection can be offered, reinforcing the positive behavior. Practicing this ritual consistently helps dogs understand that remaining on the ground is the pathway to receiving love and attention.
For those who experience occasional jumping, such as when returning home, implementing a “polite greeting” can be transformational. Segmenting practice sessions throughout the day allows for numerous opportunities to educate the dog. For instance, stepping outside briefly and returning can simulate the greets multiple times a day. Owners must be unwavering—if dogs are permitted to jump after one specific activity, they’ll begin to perceive jumping as acceptable in other scenarios.
When introducing new guests to the home, it’s vital to establish ground rules regarding jumping. Ensure that visitors are informed of the proper way to interact with your pet and discourage them from supporting jumping behavior, even through attention or laughter. Visitors should either ignore the dog or respond with calm and consistent commands, as this not only aids in training but sets a positive precedent for future interactions.
For adult dogs, approaching them at their eye level can also help manage jumping. Kneeling down for a greeting allows for a more calming interaction, and placing treats on the ground can focus their attention downward instead of encouraging them to leap up. It’s important to recognize that despite their height, the instinct to jump can persist, demanding patient and sustained effort from owners.
Finally, overcoming the jumping habit is a process that requires time, patience, and consistency. Regardless of age, every dog can learn to modify its behavior with the right training regime. Engaging in regular obedience training will further enhance impulse control and set clear expectations, making it easier for dogs to understand what is required from them.
While jumping is an innate behavior in dogs that often stems from excitement, it is essential to manage it properly to prevent potential safety concerns. With dedication, understanding, and appropriate training techniques, pet owners can cultivate a calm and respectful relationship with their canine companions, reinforcing acceptable behaviors that foster a harmonious environment.