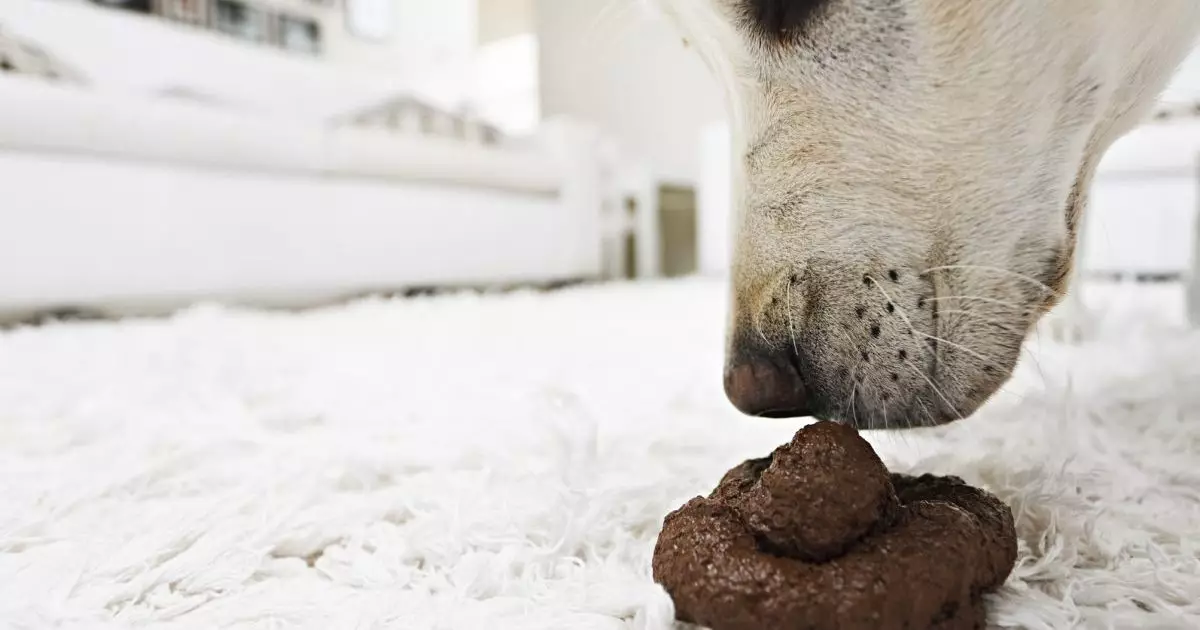
As a devoted pet owner, it’s common to experience frustration when your beloved dog exhibits behaviors that, while natural, can be downright disgusting. Among these, two habits stand out for their unpleasantness and potential health implications: coprophagia, or the act of eating feces, and scooting. While these behavioral issues can be troubling for owners, understanding their origins and implementing effective strategies can significantly improve the situation. This article delves into these issues and offers solutions aimed at reducing embarrassment and ensuring a happier, healthier dog.
Coprophagia, or the consuming of feces, is a behavior that can baffle and disgust pet owners. Despite being a natural inclination for some dogs, there are several factors that contribute to this habit. For puppies, the allure of poop can be tied to their instinctual behaviors; they often explore their environment through their mouths, and feces may appear as another potential food source. Moreover, the texture of feces can be reminiscent of the regurgitated food they received from their mother, making it a non-threatening option in their eyes.
However, the reasons behind coprophagia can extend beyond mere curiosity. Some dogs may eat feces as a way to manage anxiety or seek attention; in such cases, the behavior can become habitual if it elicits a significant response from their owners. Additionally, dogs might be drawn to feces due to nutritional deficiencies or poor diet quality. A dog’s natural inclination to consume fecal matter can escalate further in households where both dogs and cats coexist, making cat feces—typically more nutrient-rich than dog feces—an appealing snack.
While coprophagia is generally safe for most healthy, vaccinated dogs, it has its risks. Ingesting feces can increase the likelihood of parasitic infections, especially if dogs partake in neighborhood scavenging. Regular veterinary check-ups, parasite screening, and adherence to preventive treatments, such as heartworm medication, are pivotal in mitigating these risks.
Addressing coprophagia starts with understanding that it is a natural behavior for dogs. Removing the temptation for your dog is crucial. Regularly cleaning up after your dog in the yard and keeping them leashed in public spaces can significantly reduce the likelihood of them indulging in this disgusting habit.
For households with cats, it’s essential to manage access to the litter box. Options include utilizing covered litter boxes that dogs cannot access or placing the litter box in a room that dogs cannot enter, such as behind a baby gate. A diet modification can also play a pivotal role; switching to a high-protein, low-carbohydrate, and low-fat diet may deter your dog from seeking out feces. Some pet owners report success with natural deterrents like canned pineapple or spinach, which can make poop less appealing.
Throughout this process, it’s crucial to remain calm and never scold your dog for their behavior, as even negative attention can reinforce the action. Instead, focus on rewarding positive behaviors and ensuring your dog’s environment is stress-free.
Scooting is another behavior that can embarrass pet owners, often resulting in common misconceptions about its cause. Many people assume that dogs drag their bottoms across the floor due to parasites, such as worms. While this can be a contributing factor, it’s essential to consider other possibilities, primarily related to the dog’s anal glands.
Dogs have anal glands located near the base of their tail, which can become full, itchy, or inflamed, prompting them to scoot as a way to relieve discomfort. Regular grooming and veterinary care are vital in managing this issue. Veterinarians and professional groomers can express anal glands, helping to prevent the discomfort that leads to scooting.
If you notice that your dog is scooting frequently, it’s essential to monitor their behavior and consult a veterinarian if you suspect underlying health issues. Simple maintenance procedures can often alleviate this problem, allowing your dog to avoid discomfort and the shame of frequently dragging their bottom across the floor.
Understanding that behaviors such as coprophagia and scooting are rooted in natural instincts or health issues can help pet owners respond with knowledge and compassion rather than frustration. With the right strategies in place, these unpleasant habits can be managed effectively, ensuring that both dogs and their owners can enjoy a harmonious and healthy living environment. Regular veterinary care, a thoughtful approach to diet, and proactive management of your dog’s environment are essential steps in addressing and preventing these issues. By doing so, you foster a home environment that prioritizes both pet health and owner peace of mind.