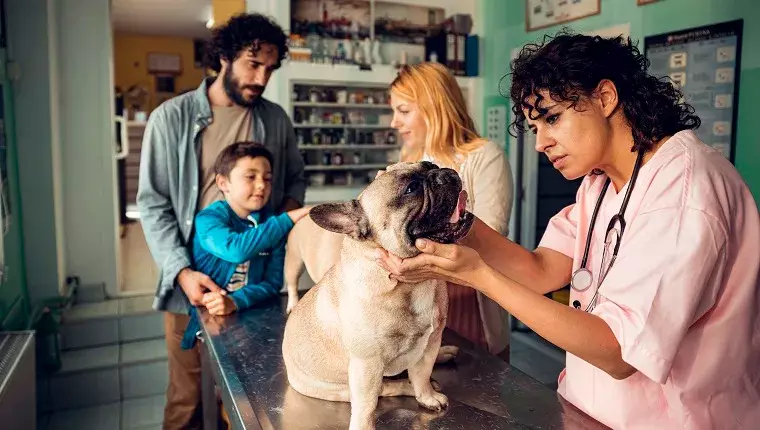
Abnormal molar development in dogs, particularly known as dilacerated mandibular first molar, is a dental issue that primarily impacts smaller dog breeds. This condition occurs when there isn’t enough space in the dog’s mouth for the molar teeth to properly erupt and align. As a result, teeth may grow at unusual angles or develop in inappropriate locations. Pet owners should remain vigilant for the signs and symptoms that may indicate their furry friend is suffering from this dental disruption.
Dogs suffering from abnormal molar development exhibit various symptoms, usually localized to the oral region. The most commonly observed signs include receding gums, which may lead to inflammation and even bleeding. The affected dog might also experience oral pain, making it difficult to chew or enjoy food, thus resulting in a reduced appetite. If you notice your dog displaying discomfort while eating or the presence of swollen and discolored gums, it’s crucial to seek veterinary advice promptly to prevent further complications.
The primary driver behind abnormal molar development in dogs is typically a constraint in space. This lack of adequate room hinders the normal growth trajectory of the teeth. Beyond spatial concerns, trauma to the mouth area—such as an injury or accident—can also contribute to the misalignment of molars. Furthermore, certain breeds are predisposed to this condition. Breeds like Boston Terriers, French Bulldogs, and Pugs frequently experience dental issues stemming from their unique jaw structures, making them more susceptible to abnormal molar growth.
If you suspect that your dog may be dealing with abnormal molar development, a comprehensive evaluation by a veterinarian is essential. The veterinarian will conduct both a detailed physical inspection and an oral examination, questioning the owner about any recent dental trauma. Diagnostic imaging, such as dental X-rays, may be utilized to gain a clearer view of the underlying issues, confirming the diagnosis and aiding in the development of an effective treatment plan.
Once diagnosed, treatment options for abnormal molar development can vary based on the severity of the condition. Pain management is typically a primary objective, and veterinarians may recommend extraction of any severely affected teeth. Post-procedure, it’s critical for pet owners to adhere to the prescribed medication regimen, including pain relievers and antibiotics, if necessary. Additionally, diet modifications may be required to ensure that the dog’s recovery process is as comfortable as possible, minimizing pain during meal times.
Abnormal molar development in dogs is an important health issue that requires immediate attention. Pet owners should be proactive in monitoring their dog’s dental health and recognizing the signs that could indicate a problem. Engaging with a veterinarian for a thorough assessment and following through with recommended treatments not only alleviates the dog’s discomfort but also fosters long-term oral health. Ensuring that your dog enjoys a pain-free life begins with staying informed and vigilant about its dental well-being.