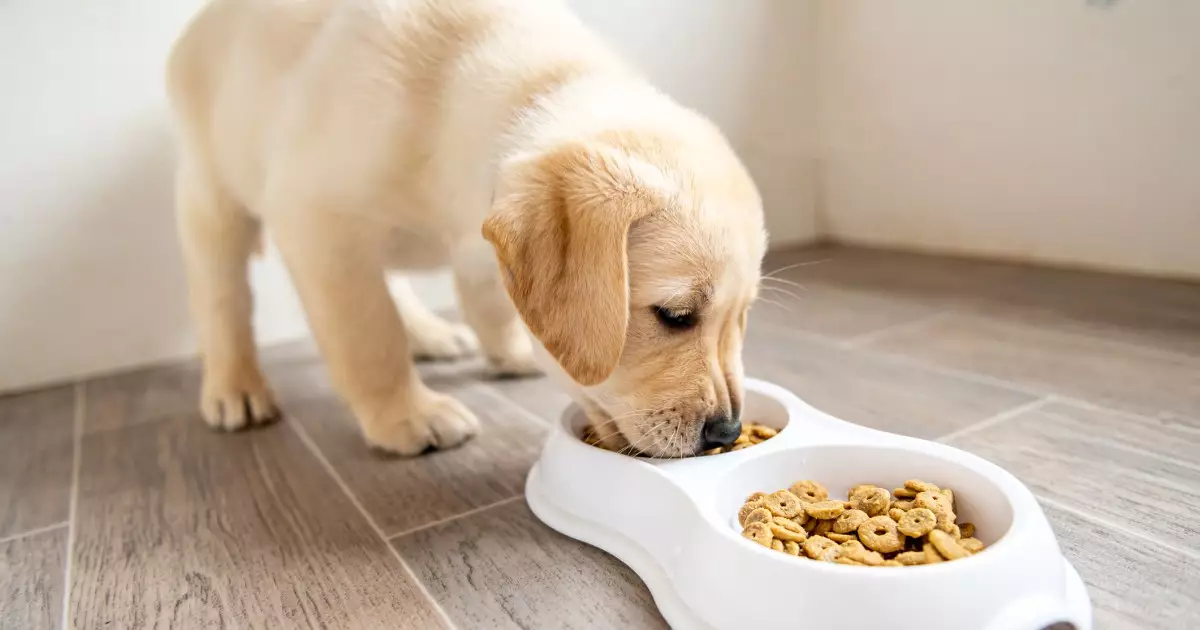
Puppies are bundles of energy and curiosity, traits that demand a robust nutritional foundation to support their rapid growth and development. Understanding how to properly feed a puppy is critical for ensuring a healthy start in life that will ultimately impact their long-term well-being.
From the moment they are born, puppies undergo significant changes. In their early months, a puppy will need to consume two to four times more food than an adult dog. This increased caloric intake is necessary to fuel their growth and the development of their organs, muscles, and bones. A good indicator of sufficient growth is to observe changes in their weight. Once a puppy reaches about one week old, they should begin to double their birth weight, and thereafter consistently gain around 1 to 2 grams for each pound of expected adult weight per day. For instance, a German Shepherd expecting to weigh 75 pounds in adulthood should ideally gain around 3 to 5 ounces daily during its puppy phase.
These nutritional needs underscore the importance of selecting the correct puppy food. Commercial puppy food varies significantly in quality; thus, it is paramount to ensure that any food chosen meets the standards set by the Association of American Feed Control Officials (AAFCO). Meeting these standards is essential, but many reputable brands go above and beyond, rigorously testing their products to enhance their nutritional profiles further. It’s important for pet owners to recognize that cheaper brands often contain lower-quality ingredients that may not provide the optimal nutrients for a growing puppy.
Puppies require distinct nutritionally balanced diets, which is why puppy food is typically richer in protein and fortified with essential vitamins, minerals, and healthy fats compared to adult dog food. Different formulas exist for various breeds and sizes. Large-breed puppy formulas are designed to ensure gradual growth, essential for avoiding skeletal issues such as hip dysplasia, while small-breed formulas offer more concentrated nutrition in smaller kibbles, essential for the high metabolic rate of tiny puppies.
Puppies of all sizes need to avoid overfeeding. A general guideline is that a puppy should have a waist when viewed from above, and their ribs should be easily felt but not prominently visible. Achieving this balance contributes to their overall health and well-being. The feeding regimes may vary; however, owners are encouraged to abide by the suggested feeding quantities provided on the packaging and make adjustments based on the puppy’s appetite and body condition.
In the early stages, typically around 8 to 12 weeks of age, puppies may consume three to four meals a day. Despite these frequent feeds, it is entirely acceptable to adjust to two meals a day if it better fits an owner’s schedule. As puppies grow and reach six months of age, it is recommended to simply feed twice a day, aligning portion sizes with their rapidly changing needs.
Another important aspect of feeding is the timing and consistency of meals. Puppies thrive on routine, and feeding at set times each day rather than leaving food available at all times helps establish a healthy eating schedule. Although some exceptions exist—for instance, very small breeds like Chihuahuas, which may be susceptible to low blood sugar and require constant access to food—most puppies benefit from structured feeding times.
While feeding a puppy may seem straightforward, several common pitfalls should be avoided. First and foremost, feeding your puppy from the table can encourage unwanted begging behaviors and lead to obesity. It’s imperative to establish boundaries concerning food and maintain consistency in feeding practices.
Furthermore, pet owners need to be cautious with portion sizes and not rush into a high-protein diet, especially for large-breed dogs. Overemphasizing protein and fat can lead to rapid growth, which presents long-term health risks. It’s crucial to find a well-balanced diet appropriate for the specific breed and size of the puppy, ensuring lasting benefits without the risks associated with inappropriate feeding customs.
Feeding a puppy requires thoughtful attention to their specific nutritional requirements and the establishment of healthy habits. By being aware of their growth stages, understanding the distinctions in puppy food formulations, and adhering to structured feeding guidelines, pet owners can provide their puppies with the foundation they need for a healthy and vibrant life. Through effective management of their dietary needs, we can cultivate healthier adult dogs capable of thriving in our homes and lives.